Uniswap in cryptocurrency has transformed the way digital assets are traded across blockchain networks. It represents one of the most powerful applications of decentralized finance (DeFi), allowing users to exchange tokens directly without relying on traditional intermediaries such as centralized exchanges. As part of the Ethereum ecosystem, it uses smart contracts to automate and secure token swaps.
Understanding Uniswap is essential for anyone exploring the cryptocurrency space. It has redefined liquidity, accessibility, and transparency within digital trading. By eliminating the need for middlemen, it empowers users with full control over their assets while providing a foundation for decentralized innovation. As cryptocurrencies continue to evolve, it remains a key player shaping the decentralized economy.
What Is Uniswap
It is an open-source decentralized exchange (DEX) protocol built on the Ethereum blockchain that automatically swaps ERC-20 tokens. Unlike traditional exchanges that depend on order books or centralized management, it uses smart contracts and liquidity pools to enable direct peer-to-peer trading.
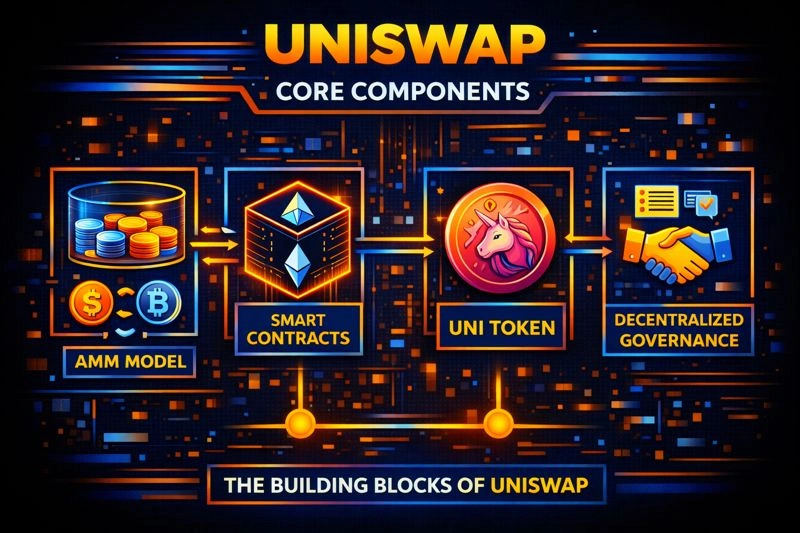
The Uniswap protocol operates under the Automated Market Maker (AMM) model. In this system, algorithms determine token prices based on supply and demand instead of relying on direct buy-and-sell orders. This setup ensures constant liquidity, allowing anyone to trade tokens at any time without waiting for a counterparty.
In the cryptocurrency industry, experts often describe Uniswap as a DeFi liquidity protocol or on-chain exchange. It enables users to provide liquidity, earn transaction fees, and join decentralized governance through its native token, UNI. Because of its efficiency, transparency, and autonomy, it has become one of the most trusted platforms in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Background Of Uniswap
It stands at the forefront of decentralized trading through its innovative Automated Market Maker (AMM) system. In this model, instead of matching buyers and sellers, it relies on liquidity pools—collections of tokens supplied by users—to facilitate trades.
This formula ensures that as the supply of one token increases, its price rises relative to the other, maintaining balance within the pool. This mechanism allows traders to execute swaps instantly without needing a counterpart, revolutionizing how cryptocurrency exchanges function.
Liquidity providers (LPs) play a central role in Uniswap’s ecosystem. They deposit equal values of two tokens into a pool and, in return, earn a portion of the trading fees generated by the pool. This model creates a decentralized, self-sustaining marketplace.
It also operates entirely on smart contracts, ensuring transparency and security. Each transaction is executed automatically by code, removing human bias and central authority. The platform’s design supports interoperability, allowing tokens to be easily integrated with other decentralized applications (dApps).
Over time, Uniswap has evolved through multiple versions. Uniswap V2 introduced direct ERC-20 to ERC-20 swaps, while V3 implemented concentrated liquidity, enabling liquidity providers to allocate capital within specific price ranges for greater efficiency. The upcoming V4 aims to further reduce gas fees and provide greater customization for liquidity pools.
It’s governance is driven by its UNI token, which grants holders voting power over protocol updates, fee structures, and future developments. This decentralized decision-making process strengthens community participation and keeps the ecosystem adaptable to market needs.
History or Origin of Uniswap
It was founded by Hayden Adams in 2018, inspired by a concept proposed by Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin on automated market makers (AMMs). The project began as a simple experiment to create a decentralized exchange using smart contracts. However, it quickly gained traction due to its simplicity, transparency, and effectiveness.
The first version, Uniswap V1, allowed users to trade any ERC-20 token against Ether (ETH). Later, in 2020, the launch of Uniswap V2 expanded the protocol to support ERC-20 to ERC-20 swaps, improving both flexibility and user adoption. During the same year, Uniswap introduced its UNI governance token, granting holders the power to influence the platform’s future through decentralized voting.
In 2021, the release of Uniswap V3 marked another milestone. It introduced concentrated liquidity and multiple fee tiers, allowing liquidity providers to manage risk more precisely and maximize capital efficiency. As a result, Uniswap strengthened its position as a global leader in decentralized exchanges.
Since then, it has continued to evolve. It has integrated with Layer 2 scaling solutions such as Optimism, Arbitrum, and Polygon, which significantly improved transaction speed while reducing gas costs. Moreover, these integrations made Uniswap more accessible to users seeking faster and cheaper trading options.
The upcoming V4 release further advances Uniswap’s mission to make decentralized trading more efficient and user-friendly. It aims to lower gas fees, enhance customization, and streamline the creation of liquidity pools. Consequently, Uniswap continues to set new standards in decentralized exchange technology.
Overall, Uniswap’s remarkable growth reflects the broader evolution of the cryptocurrency industry—from a niche experiment into a global, transparent, and decentralized financial ecosystem. Its steady innovation, combined with community-driven governance, has turned Uniswap into a cornerstone of the modern DeFi movement.
Types of Uniswap
Uniswap has evolved through several versions, each designed to improve functionality, efficiency, and flexibility. While all versions follow the same decentralized exchange model, they introduce distinct enhancements.
Uniswap V1 was the original implementation. It allowed users to trade ERC‑20 tokens only against Ether (ETH). Although simple, it proved the viability of automated liquidity.
Uniswap V2 expanded the protocol by enabling direct ERC‑20 to ERC‑20 swaps. It also improved price accuracy and reduced reliance on ETH as an intermediary asset. This version significantly increased adoption across the decentralized finance ecosystem.
Uniswap V3 introduced concentrated liquidity and multiple fee tiers. Liquidity providers gained greater control over capital allocation, which improved returns and reduced inefficiencies. The upcoming Uniswap V4 focuses on lowering gas fees and increasing customization through advanced smart contract hooks.
How Does Uniswap Work?
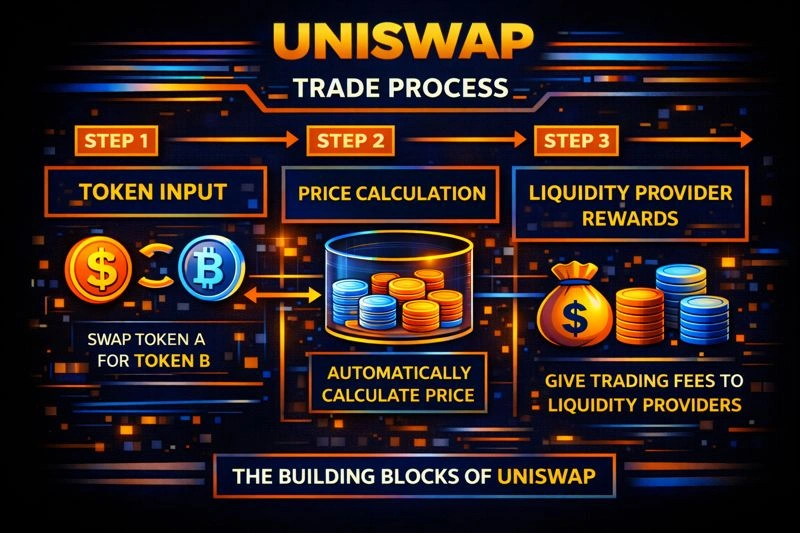
Uniswap operates by using liquidity pools instead of traditional order books. First, users supply equal values of two tokens into a pool. These pools act as the source of liquidity for traders.
Next, when a user initiates a trade, the protocol uses an algorithmic pricing formula to determine the exchange rate. This formula adjusts prices automatically based on supply and demand within the pool.
After the trade executes, a small fee is charged. This fee is then distributed to liquidity providers as a reward. All transactions are handled by smart contracts, ensuring transparency and security. Because everything happens on-chain, Uniswap enables fast, permissionless, and trust-minimized trading.
Pros and Cons
Uniswap offers clear advantages, but it also presents certain challenges. Understanding both helps users make informed decisions.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Fully decentralized trading | Exposure to impermanent loss |
| No intermediaries or custodians | Ethereum gas fees can be high |
| Permissionless access | Limited protection against volatility |
| Transparent smart contracts | Requires basic DeFi knowledge |
Applications or Uses of Uniswap
It has numerous applications within decentralized finance and beyond. In crypto trading, it allows users to instantly swap tokens without relying on centralized exchanges. AI algorithms enhance this process by identifying the best liquidity pools, predicting price movements, and executing trades with precision.
In liquidity provision, users can deposit assets into pools to earn transaction fees. AI can analyze liquidity patterns to suggest optimal pool allocations, minimizing impermanent loss while maximizing yield. This is particularly valuable in volatile markets where human decision-making can lag behind rapid changes.
Uniswap’s governance model also benefits from artificial intelligence. Machine learning can evaluate community proposals, simulate outcomes, and assist UNI holders in making informed voting decisions.
In portfolio management, AI-powered DeFi dashboards integrate with Uniswap APIs to track performance, automate trading, and balance risk exposure across different tokens. This automation allows investors to engage in decentralized trading without constantly monitoring the markets.
Additionally, Uniswap plays a crucial role in Web3 ecosystems, serving as a liquidity backbone for decentralized applications (dApps) and NFT marketplaces. By combining Uniswap’s data with AI analytics, developers can gain insights into market sentiment, token velocity, and liquidity depth, further refining DeFi systems.
In essence, Uniswap demonstrates how artificial intelligence can complement blockchain innovation—creating a smarter, more adaptive, and user-centered financial network.
Resources
- Uniswap: Official Website
- Ethereum Foundation: Understanding Automated Market Makers
- GitHub Repository: Uniswap Protocol Source Code
- CoinDesk: The Evolution of Uniswap and DeFi
- Medium: How AI is Transforming Uniswap and DeFi