A Liquidity Pool is a core concept in modern decentralized finance and plays a vital role in how crypto markets function today. As blockchain-based platforms move away from traditional intermediaries, this model ensures that users can exchange assets quickly and efficiently. Instead of relying on buyers and sellers to match orders, decentralized systems depend on pooled funds that remain available at all times.
In the broader Cryptocurrency ecosystem, liquidity determines how easily assets can be exchanged without causing major price changes. Liquidity Pool mechanisms solve common problems such as low volume and delayed execution. They also allow regular users to participate by contributing funds, rather than leaving market activity only to large institutions.

This article explains Liquidity Pool fundamentals in a clear and practical way. You will learn what it means, how it developed, and why it matters in crypto markets. It also covers types, components, benefits, risks, and real-world applications. By the end, you will have a strong foundation to understand how liquidity pools support decentralized platforms.
What is Liquidity Pool?
A Liquidity Pool is a collection of digital assets locked inside a smart contract. These assets are used to facilitate instant swaps on decentralized platforms. Rather than matching buyers and sellers directly, the system uses algorithms to determine prices based on the ratio of assets in the pool.
The main purpose of a Liquidity Pool is to maintain continuous liquidity. This means users can exchange tokens at any time without waiting for another participant. As trades occur, the balance of assets changes, and prices adjust automatically. This process removes the need for centralized order books.
Liquidity pools are closely tied to automated market makers, often called AMMs. These systems rely on mathematical formulas to set prices instead of market bids. When one asset is added or removed, the formula updates the exchange rate to reflect supply and demand.
Within the crypto industry, Liquidity Pool models improve transparency and accessibility. Anyone with a compatible Crypto wallet can interact with them. This open design supports decentralization while keeping markets active and efficient.
Background of Liquidity Pool
Liquidity Pool systems consist of several interconnected elements that work together to support decentralized exchanges. Each component plays a specific role in maintaining balance and reliability.
At the center is the smart contract. It securely holds the pooled assets and enforces the rules of the system. These contracts are designed to be transparent and automated, reducing the need for trust between participants.
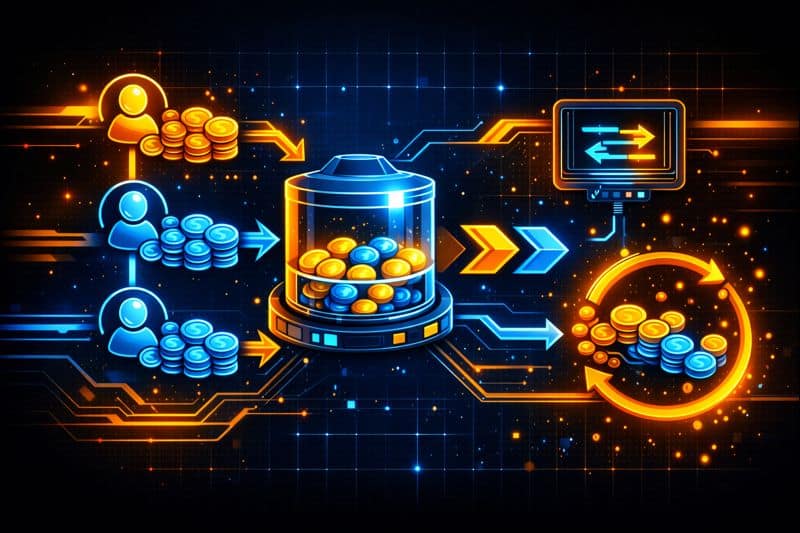
Another key element is the asset pair. Most pools require two tokens of equal value to function. These paired assets allow users to swap one token for another based on the pool’s current ratio.
Pricing algorithms are also essential. They calculate exchange rates using predefined formulas. As one asset is traded, the price adjusts to prevent imbalance. This approach keeps liquidity available even during periods of high demand.
User participation supports the entire system. Individuals deposit funds into pools and earn a share of transaction fees. In this way, the pool rewards contributors while enabling Trading for others.
List of Key Components or Aspects:
- Smart contracts that lock and manage assets
- Paired digital assets used for swaps
- Automated pricing formulas
- Fee distribution mechanisms for contributors
History of Liquidity Pool
The Liquidity Pool concept emerged as a response to limitations in early decentralized exchanges. Traditional order-book models struggled with low volume and inefficient trade execution. Developers needed a system that could function without centralized oversight.
Automated market makers gained attention around 2018. These systems introduced liquidity pools as a solution to liquidity shortages. Instead of waiting for counterparties, trades could occur instantly using pooled assets.
The model gained widespread adoption during the growth of decentralized finance in 2020. Platforms built entire ecosystems around liquidity pools, offering incentives to attract contributors. As usage expanded, the design evolved to include new pool structures and risk management tools.
Today, Liquidity Pool mechanisms are a standard feature across many blockchain networks. They continue to support innovation in decentralized applications.
| Period | Key Development |
|---|---|
| Pre-2018 | Order-book dominance on exchanges |
| 2018 | Introduction of AMM-based pools |
| 2020 | Rapid growth of DeFi platforms |
| 2021 onward | Expansion and refinement |
Types of Liquidity Pool
Liquidity Pool designs vary based on their purpose and risk profile. Each type serves different user needs within decentralized systems.
One common type involves volatile asset pairs. These pools support active markets and often offer higher rewards. However, they also carry greater exposure to price changes.
Stable asset pools focus on tokens with similar values. Because prices move less dramatically, these pools aim to reduce risk. They are often used for low-slippage swaps and predictable returns.
Single-asset pools allow contributors to deposit one token instead of two. The protocol balances exposure internally. This approach simplifies participation but may involve additional system complexity.
There are also multi-asset pools that support more than two tokens. These pools enable advanced strategies and flexible pricing models. Each type operates through smart contracts but follows different rules and incentives.
How Does Liquidity Pool Work?
A Liquidity Pool begins when users deposit assets into a smart contract. Typically, contributors add two tokens of equal value. Once deposited, these funds form a shared reserve available for swaps.
When a user initiates a trade, the pool exchanges one asset for another. The pricing algorithm recalculates rates based on the new balance. This ensures that liquidity remains available even as demand changes.
Each transaction includes a fee. These fees accumulate and are distributed among contributors based on their share of the pool. Over time, this system encourages users to provide liquidity and maintain market stability.
The entire process runs automatically. Smart contracts enforce rules, handle calculations, and manage payouts without manual intervention.
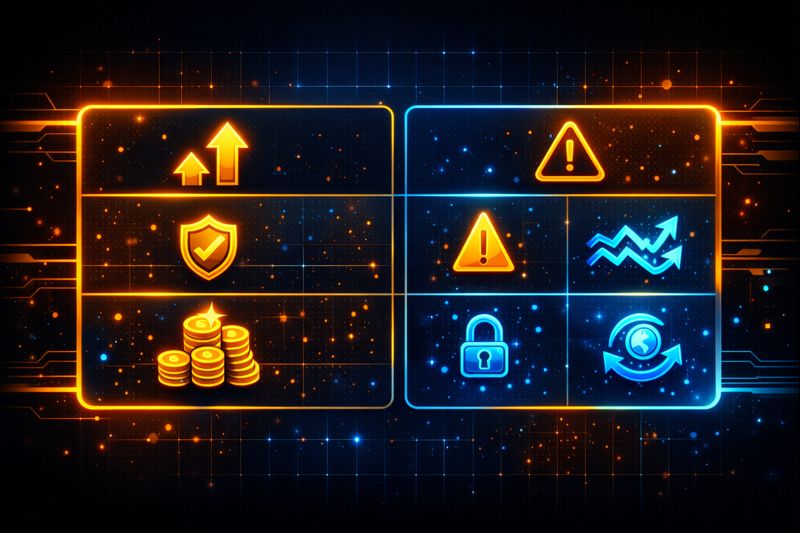

Pros and Cons of Liquidity Pool
Liquidity Pool models offer clear advantages but also introduce specific risks. Understanding both sides helps users evaluate participation.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Always-on liquidity | Exposure to impermanent loss |
| Decentralized and transparent | Smart contract risks |
| Enables passive income | Impact from market volatility |
Applications of Liquidity Pool
Liquidity Pool systems support many practical crypto use cases. They form the backbone of decentralized exchanges by enabling fast and permissionless swaps.
Decentralized Exchanges
Most decentralized exchanges rely on liquidity pools instead of order books. This setup allows users to trade directly from their wallets without intermediaries.
DeFi Services
Liquidity pools support lending, borrowing, and yield strategies. They provide the liquidity needed for these services to function smoothly.
Token Distribution
New projects often use pools to launch tokens and establish initial market liquidity. This approach promotes fair access and price discovery.
These applications show how Liquidity Pool models continue to shape the crypto landscape.
Resources
CryptoRobotics.ai. What Are Liquidity Pools? AMM Mechanics Explained
Keyrock. Guide to Liquidity Pool Management
C-Sharp Corner. What Is a Liquidity Provider in Crypto and How Does It Work?
Changelly. What Are Liquidity Pools?
GeeksforGeeks. What Are Liquidity Pools in Crypto?

